JSON-LD Schema for SEO: What Marketers Should Know
Are you scratching your head over JSON-LD? You’re hardly alone. Although it sounds technical, JSON-LD plays a pivotal role in how search engines parse and present your content. In this post, we’ll unpack what JSON-LD is, where to place it, common pitfalls, and how it can help your site win better visibility in search results.
What Is JSON-LD?
JSON-LD (JavaScript Object Notation for Linked Data) is a format that helps websites express structured data in a way search engines can easily understand. It’s based on the syntax of traditional JSON but adds context so machines can interpret meaning. That’s why Google and other major search engines accept JSON-LD—you’re not just sending raw data, you’re describing what it means.
By using JSON-LD, your pages can become eligible for features like rich snippets, knowledge graphs, FAQ boxes, and more. Because the data is decoupled from visible HTML, it tends to cause fewer conflicts or markup errors.
How JSON-LD Works in Your Pages
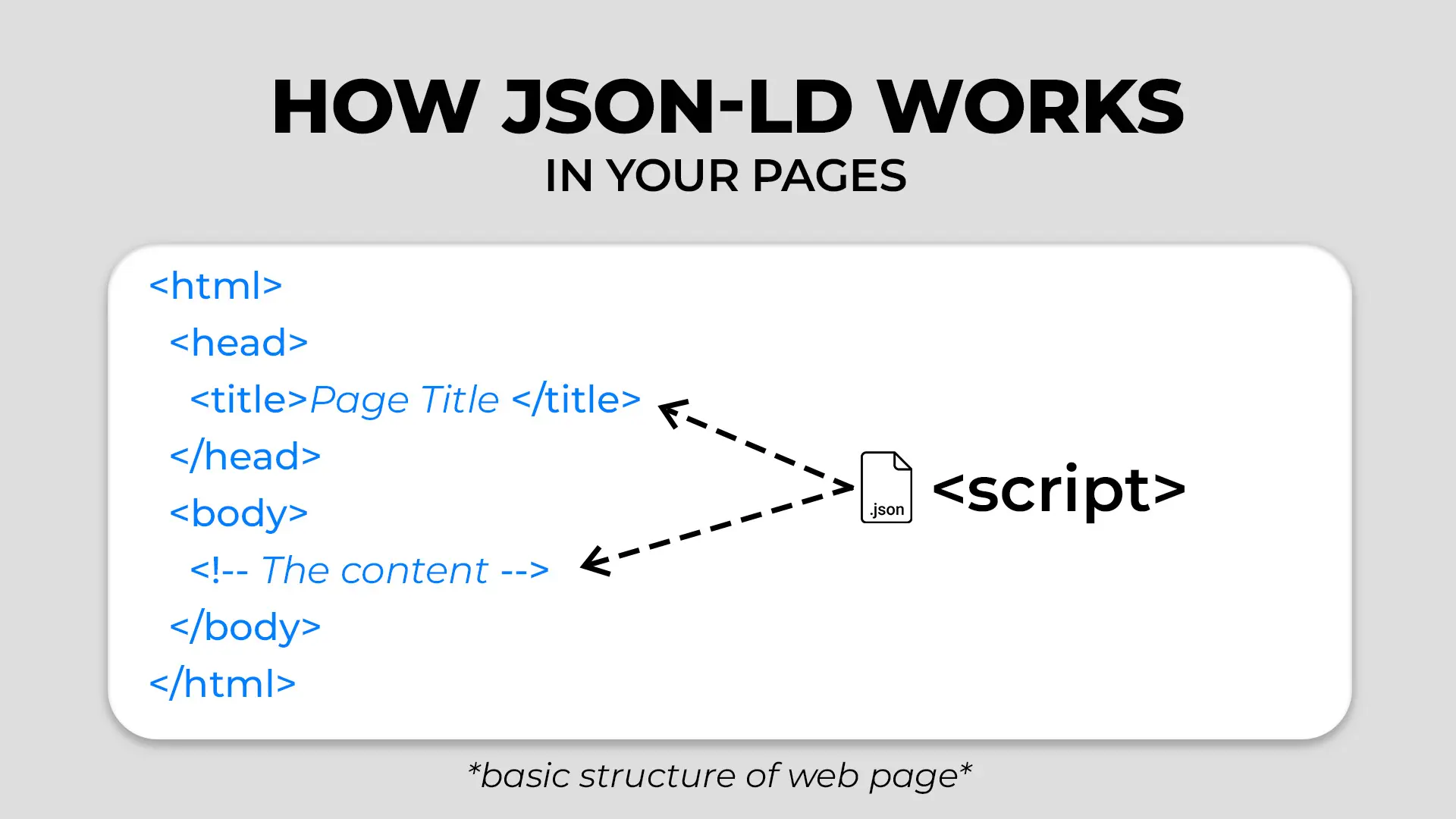
Essentially, JSON-LD lets you embed structured data (using schema.org vocabulary) in a <script> tag:
<script type="application/ld+json">
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "Article",
"headline": "Your Article Title",
"author": {"@type": "Person", "name": "Your Name"},
"datePublished": "2025-10-01"
}
</script>
You may place that <script> block in either the <head> or <body> of your HTML. Google can interpret it in either spot—even if it’s loaded dynamically via JavaScript—though embedding it early in the <head> can reduce risk of it being missed.
Nesting in JSON-LD
Nesting means structuring information in layers. For example, if an article has an author and the author has social profiles, your JSON-LD might look like:
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "Article",
"headline": "Your Title",
"author": {
"@type": "Person",
"name": "Jane Doe",
"sameAs": ["https://twitter.com/janedoe"]
}
}
Here, author is nested under the main Article object. Nesting gives context and relationships that help search engines map how parts relate.
JSON-LD vs. JSON: What’s the Difference?
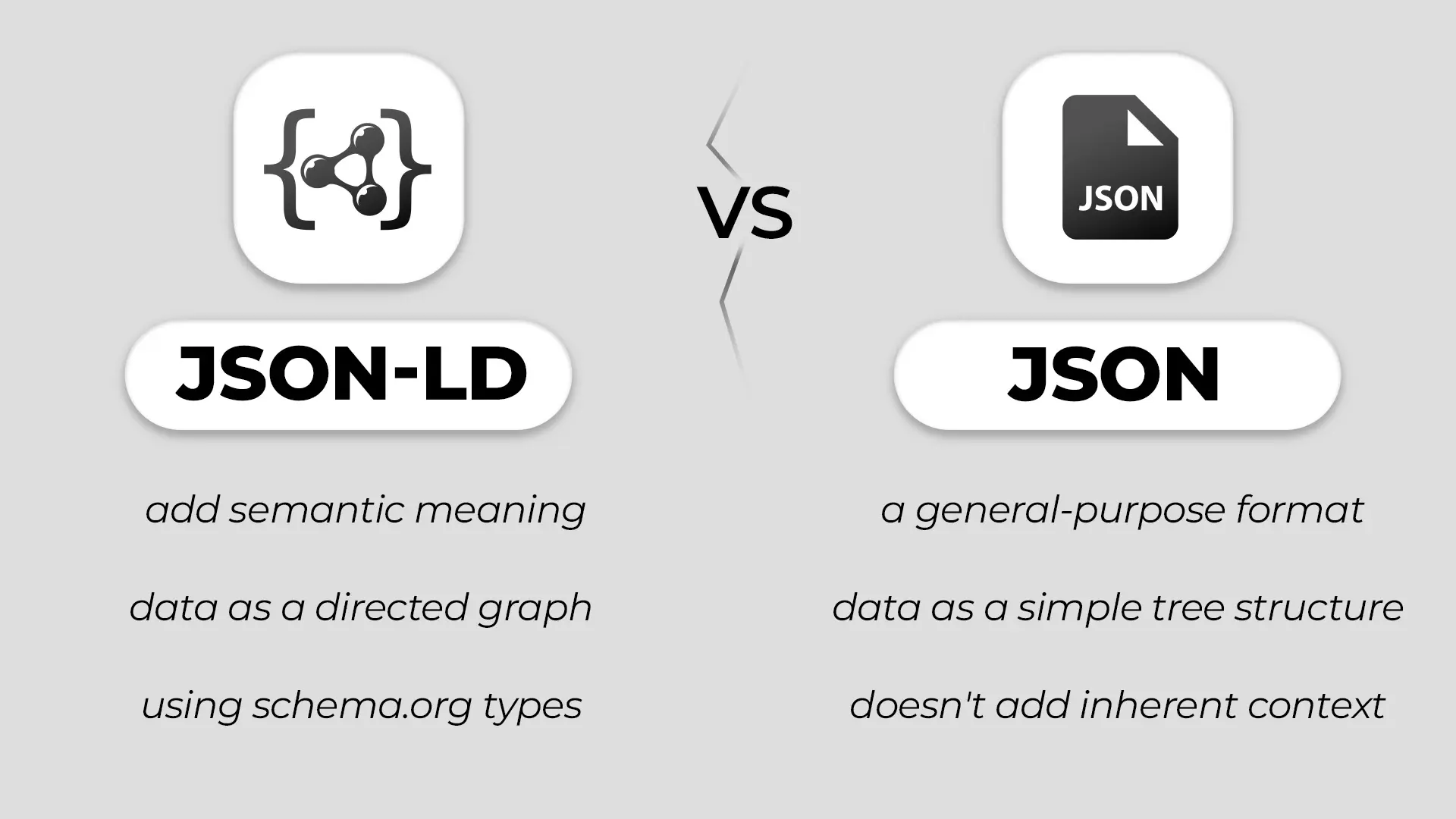
- JSON is a general-purpose data format used in many environments.
- JSON-LD, in contrast, adopts JSON’s syntax but adds semantics—“this is a Person,” “this is an Article,” etc.—using schema.org types. That extra layer of meaning is what search engines use to create rich displays.
Thus, JSON-LD is more SEO-friendly: it lets you declare what things are, not just what they are called.
Common Mistakes to Watch Out For

- Syntax errors – mismatched braces, missing commas, wrong quotation marks.
- Wrong vocabulary – using properties not allowed under a schema type (always check schema.org).
- Data mismatch – your JSON-LD must align with visible content (e.g. datePublished should match the page).
- Injection errors – copying text from editors like Word can introduce hidden characters.
- Overlapping markup – if you use both JSON-LD and microdata for the same content, Google may ignore one.
What SEO Changes Can You See After Implementation?
If done correctly, JSON-LD can unlock richer search results, such as:
- Review stars / rating snippets
- FAQ blocks
- Event information (time, location)
- Organization or local business panels
- Better article previews (with images, date, author)
Reports suggest pages with structured data can see CTR lifts of up to 20–30%, although results depend heavily on competition and schema type.
Testing Your Implementation
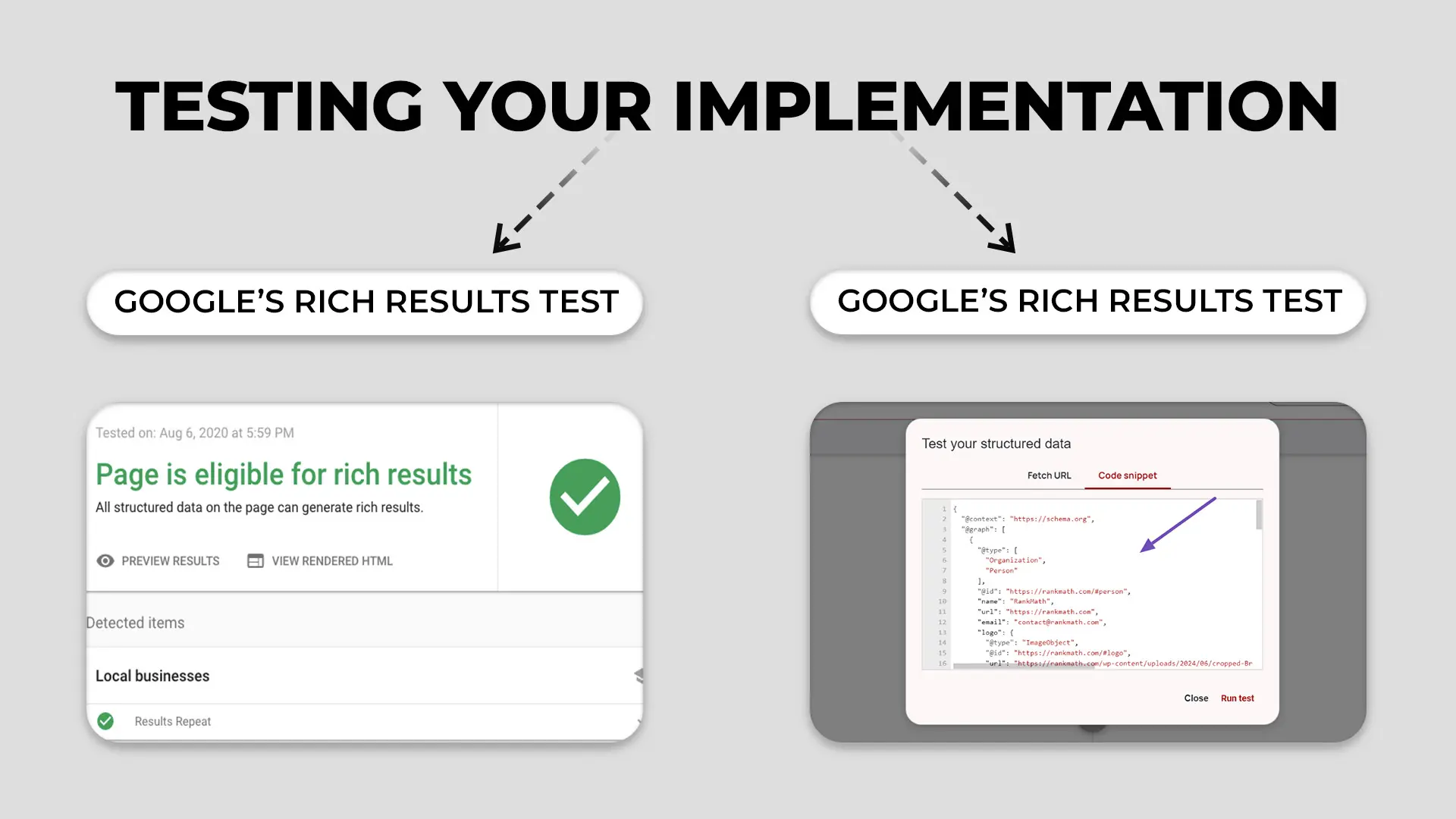
You can check your JSON-LD with:
- Google’s Rich Results Test – see which rich snippets your markup qualifies for
- Schema Markup Validator – validate syntax and schema.org compatibility
Always test in multiple page types (home, blog, product) and monitor Search Console for errors or warnings.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Does JSON-LD guarantee rich results? No. Even well-formed markup doesn’t guarantee Google will display a rich result—Google considers many factors like page quality, SERP context, and relevance.
2. Can I use JSON-LD with microdata or RDFa? Yes, but redundancy or conflicts may confuse search engines. Google generally prefers JSON-LD.
3. Is JSON-LD supported by Google? Absolutely. Google recommends JSON-LD when site setup allows it.
Summary
JSON-LD is a powerful, flexible way to provide structured, meaningful data to search engines without complicating your visible markup. When correctly implemented, it can improve chances for rich results and boost click-through rates.
For your best results:
- validate your markup often
- align JSON-LD with your visible content
- follow Google’s structured data guidelines
- avoid redundant or conflicting schemas
As Google continues evolving toward more semantic, context-aware search, adopting JSON-LD now ensures your content is future-ready.
Sample JSON-LD for an Article
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "Article",
"headline": "Json-LD Schema for SEO: What Marketers Should Know",
"author": {
"@type": "Person",
"name": "Your Name",
"sameAs": ["https://twitter.com/yourhandle"]
},
"datePublished": "2025-10-08",
"image": "https://yourdomain.com/image.jpg",
"publisher": {
"@type": "Organization",
"name": "Your Blog",
"logo": {
"@type": "ImageObject",
"url": "https://yourdomain.com/logo.png"
}
}
}